Bianchini
Contents
Bianchini
|
Lat: 48.77°N, Long: 34.4°W, Diam: 37.59 km, Depth: 3.1 km, Rükl: 2, Upper Imbrian |
Table of Contents
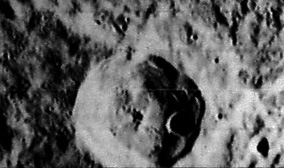
Lunar Orbiter IV-145-h3
Images
LPOD Photo Gallery Lunar Orbiter Images
Maps
(LAC zone 11C4) LAC map Geologic map
Description
Elger
(IAU Directions) BIANCHINI.--A fine ring-plain, about 18 miles in diameter, on the N.W. side of the Sinus Iridum, surrounded by the lofty mountains defining the border of the bay. Its walls, which are prominently terraced within, rise about 7,000 feet on the W., and about 8,000 feet on the E. above the floor, which includes a prominent ridge and a conspicuous central mountain. There is a distinct crater on the S. wall, not shown in the maps. Between this side of the formation and the bay is a number of hills running parallel to the shore-line: these, with the intervening valleys, will repay examination at sunrise.
Wikipedia
Additional Information
- IAU page: Bianchini
- Depth data from Kurt Fisher database
- Westfall, 2000: 3.1 km
- Viscardy, 1985: 3.05 km
Nomenclature
- Named for Francesco Bianchini (December 13, 1662 – March 2, 1729), an Italian philosopher and scientist. He worked for the curia of three popes, including being camiere d`honore of Clement XI, and secretary of the commission for the reform of the calendar, working on the method to calculate the astronomically correct date for Easter in a given year. As part of his efforts to improve the accuracy of the calendar, Bianchini constructed an important meridian line in the basilica of Santa Maria degli Angeli e dei Martiri in Rome, a device for calculating the position of the sun and stars.
- In 1728, Bianchini published a book regarding his observations of Venus which included his observation of sunrise over Plato as well as what is thought to be the first ever depiction of the lunar Alpine Valley.
- Comments on Bianchini's lunar drawing from exhibit at Linda Hall Library.
LPOD Articles
Bibliography
- Bianchini, Francesco. 1728. Hesperi et phosphori nova phaenomena sive observationes circa planetan Veneris. Romae: Joannem Mariam Salvioni. (scanned copy at ETH-rara)
Francesco Bianchini in the Sourcebook Project (William R. Corliss)
- In Mysterious Universe, a handbook of astronomical anomalies (1979) :
- Page 100: On the Visibility of the Dark Side of Venus (A.Schafarik, Report of the British Association, 1873).
- Page 110: Illusions (E.M.Antoniadi, Journal of the British Astronomical Association, 1897).
- Page 118: The Radial Markings of Venus: another point of view (Patrick Moore, Strolling Astronomer, 1955).
- Page 129: Notes on the Rotation Period of Venus (E.M.Antoniadi, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 1898).
Named Featues -- Prev: Bi Sheng -- Next: Biela
This page has been edited 1 times. The last modification was made by - tychocrater tychocrater on Jun 13, 2009 3:24 pm - afx3u3