Difference between revisions of "Bullialdus"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{| class="wiki_table" | {| class="wiki_table" | ||
| colspan="3" | | | colspan="3" | | ||
| − | Lat: 20.74°S, Long: 22.36°W, Diam: 60.72 km, Depth: 3.51 km, [ | + | Lat: 20.74°S, Long: 22.36°W, Diam: 60.72 km, Depth: 3.51 km, [[R%C3%BCkl%2053|Rükl: 53]], [[Stratigraphy|Upper Imbrian]]<br /> |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
==Maps== | ==Maps== | ||
| − | ''([ | + | ''([[LAC%20zone|LAC zone]] 94A3)'' [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/resources/mapcatalog/LAC/lac94/ LAC map] [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/resources/mapcatalog/usgs/I485/ Geologic map]<br /> <br /> |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
===Elger=== | ===Elger=== | ||
| − | ''([ | + | ''([[IAU%20Directions|IAU Directions]])'' BULLIALDUS.--A noble object, 38 miles in diameter, forming with its surroundings by far the most notable formation on the surface of the [[Mare%20Nubium|Mare Nubium]], and one of the most characteristic ring-plains on the moon. It should be observed about the time when the morning terminator lies on the E. border of the [[Mare%20Humorum|Mare Humorum]], as at this phase the best view is obtained of the two deep parallel terrace valleys which run round the bright inner slope of the W. wall, of the crater-row against which they abut on the S.W., and of the massive E. <u>glacis</u>, with its spurs and depressions. The S. border of Bullialdus has been manifestly modified by the presence of the great ring-plain A, a deep irregular formation with linear walls, which is connected with it by a shallow valley. The rampart of Bullialdus rises about 8,000 feet above a concave floor, which sinks some 4,000 feet below the Mare on the W. With the exception of the fine compound central mountain, 3,000 feet high, there are few details in the interior. On the S., is the fine ring-plain B, connected with the S.W. wall near the crater-row by a well-marked valley, and nearly due W. of B is another, a square-shaped enclosure, C, with a very lofty little mountain on the W. side of it, and a crater on its S. wall. In addition to these features, there are many ridges and surface inequalities, very prominent under oblique illumination.<br /> <br /> |
===Wikipedia=== | ===Wikipedia=== | ||
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bullialdus_%28crater%29 Bullialdus]<br /> <br /> | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bullialdus_%28crater%29 Bullialdus]<br /> <br /> | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
* IAU page: [http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/917 Bullialdus] | * IAU page: [http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/917 Bullialdus] | ||
| − | * Depth data from [ | + | * Depth data from [[Kurt%20Fisher%20crater%20depths|Kurt Fisher database]] |
** Westfall, 2000: 3.51 km | ** Westfall, 2000: 3.51 km | ||
** Viscardy, 1985: 3.51 km | ** Viscardy, 1985: 3.51 km | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
** '''Central Peak Height'''(above average floor level) = 0.8 km | ** '''Central Peak Height'''(above average floor level) = 0.8 km | ||
* Central peak height | * Central peak height | ||
| − | ** [ | + | ** [[Wood%2C%201971|Wood, 1971]]: 1.11 km <span class="membersnap">- [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/tychocrater [[Image:tychocrater-lg.jpg|16px|tychocrater]]] [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/tychocrater tychocrater] <small>Mar 17, 2008</small></span> |
| − | * [ | + | * [[Central%20peak%20composition|Central peak composition]]: GNTA1, GNTA2, AN & N ([[Tompkins%20%26%20Pieters%2C%201999|Tompkins & Pieters, 1999]]) |
| − | * West rim slope 46° ([ | + | * West rim slope 46° ([[Pohn%2C%201963|Pohn, 1963]]) |
* Stratigraphy changed to Upper Imbrian based on Galileo data and crater counts ([http://www.agu.org/pubs/crossref/1993/93JE01137.shtml McEwen et al, 1993]) | * Stratigraphy changed to Upper Imbrian based on Galileo data and crater counts ([http://www.agu.org/pubs/crossref/1993/93JE01137.shtml McEwen et al, 1993]) | ||
| − | * Note the wonderfully impacted display (yellow box in the large image version below - ''click image'') of lighter material from this [http://wms.lroc.asu.edu/lroc/view_lroc/LRO-L-LROC-2-EDR-V1.0/M120004880ME WAC] view showing a region northwest of '''Bullialdus B'''. Did a chunk from [ | + | * Note the wonderfully impacted display (yellow box in the large image version below - ''click image'') of lighter material from this [http://wms.lroc.asu.edu/lroc/view_lroc/LRO-L-LROC-2-EDR-V1.0/M120004880ME WAC] view showing a region northwest of '''Bullialdus B'''. Did a chunk from [[Tycho|Tycho]]'s (to the south-east) ejecta clip the rim; sending out material across the darker ejecta plain of '''Bullialdus''' crater?. There also is an additional feature to look out for here just south of '''Bullialdus''' crater itself (red box in larger version image), where upto five fingers of lighter-looking deposits (again, possibly due to ejecta material-chunks from '''Tycho''' crater) has directionally, and dynamically, aligned itself back to that crater. ''[http://lroc.sese.asu.edu/index.html LROC]'' images (WAC No.s (left image) [http://wms.lroc.asu.edu/lroc/view_lroc/LRO-L-LROC-2-EDR-V1.0/M120004880ME M120004880ME] and (right image) [http://wms.lroc.asu.edu/lroc/view_lroc/LRO-L-LROC-2-EDR-V1.0/M117643256ME M117643256ME]). Calibrated by [http://ltvt.wikispaces.com/Utility%20Programs#WAC_Viewer LROC_WAC_Previewer]<span class="membersnap">- [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/JohnMoore2 [[Image:JohnMoore2-lg.jpg|16px|JohnMoore2]]] [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/JohnMoore2 JohnMoore2]</span><br /> [http://the-moon.us/wiki/file/detail/bullialdus-bc.jpg [[Image:bullialdus-bc-small.jpg|bullialdus-bc-small.jpg]]] |
* A certain Whitley discovered several chains of minute craters southeast of '''Bullialdus''', see page 136 in T.W.Webb's ''Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes'' (Volume 1; ''The Solar System'', chapter THE MOON). <span class="membersnap">- [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/DannyCaes [[Image:DannyCaes-lg.jpg|16px|DannyCaes]]] [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/DannyCaes DannyCaes] <small>Jul 11, 2015</small></span> | * A certain Whitley discovered several chains of minute craters southeast of '''Bullialdus''', see page 136 in T.W.Webb's ''Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes'' (Volume 1; ''The Solar System'', chapter THE MOON). <span class="membersnap">- [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/DannyCaes [[Image:DannyCaes-lg.jpg|16px|DannyCaes]]] [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/DannyCaes DannyCaes] <small>Jul 11, 2015</small></span> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
* Named for [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ismael_Bullialdus Ismaël Boulliau] (September 28, 1605 - November 25, 1694), a French priest, librarian and astronomer. Boulliau's name has apparently also (but incorrectly according to this 19th century [http://web.clas.ufl.edu/users/rhatch/pages/11-ResearchProjects/boulliau/bio-historical/06-b-michaud-1843-etc.htm French encyclopedia]) been spelled '''Bouillaud'''. It is for his astronomical and mathematical works that Boulliau is best known. Among them in his ''Astronomia philolaica'', published in 1645 and famous for the passage in which he proposed that the force of gravity follows an inverse-square law. | * Named for [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ismael_Bullialdus Ismaël Boulliau] (September 28, 1605 - November 25, 1694), a French priest, librarian and astronomer. Boulliau's name has apparently also (but incorrectly according to this 19th century [http://web.clas.ufl.edu/users/rhatch/pages/11-ResearchProjects/boulliau/bio-historical/06-b-michaud-1843-etc.htm French encyclopedia]) been spelled '''Bouillaud'''. It is for his astronomical and mathematical works that Boulliau is best known. Among them in his ''Astronomia philolaica'', published in 1645 and famous for the passage in which he proposed that the force of gravity follows an inverse-square law. | ||
| − | * According to [ | + | * According to [[Whitaker|Whitaker]] (p. 211), the crater name, in the Latinized form '''Bullialdus''', has continued unchanged since its original use on [[Riccioli|Riccioli]]'s map. |
| − | * Mary Blagg, in her ''[ | + | * Mary Blagg, in her ''[[Collated%20List|Collated List]]'' (1913) noted that the feature name was spelled '''Bullialdus''' by [[Neison%2C%201876|Neison, 1876]] and Schmidt, but '''Bulliald''' by [[Beer%20and%20M%C3%A4dler|Beer and Mädler]] (possibly a misprint in her catalog?). |
| − | * Curiously, the name is printed and listed as '''Bouillaud''' on [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/resources/mapcatalog/LTM/sheet_2/ Sheet 2] of the Army Map Service's [ | + | * Curiously, the name is printed and listed as '''Bouillaud''' on [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/resources/mapcatalog/LTM/sheet_2/ Sheet 2] of the Army Map Service's [[LTM|LTM]] series (prepared in 1963), which claims to adhere strictly to the then-current [[IAU%20nomenclature|IAU nomenclature]]. Why the map makers thought the IAU name had been changed to this (incorrect) non-Latinized form is unclear. It does not seem to have been used in that way on any other maps of the period. <span class="membersnap">- [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/JimMosher [[Image:JimMosher-lg.jpg|16px|JimMosher]]] [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/JimMosher JimMosher]</span> |
| − | * I have the 1935 [ | + | * I have the 1935 [[Named%20Lunar%20Formations|IAU map and catalog]] where the name appears as '''Bullialdus'''; apparently the LTM list is not an error-free transcription. <span class="membersnap">- [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/tychocrater [[Image:tychocrater-lg.jpg|16px|tychocrater]]] [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/tychocrater tychocrater] <small>Aug 1, 2007</small></span> |
* Why are there no officially recognized names for two pronounced craters south of '''Bullialdus'''? (still called '''Bullialdus A''' and '''Bullialdus B'''). <span class="membersnap">- [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/DannyCaes [[Image:DannyCaes-lg.jpg|16px|DannyCaes]]] [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/DannyCaes DannyCaes] <small>Apr 29, 2017</small></span> | * Why are there no officially recognized names for two pronounced craters south of '''Bullialdus'''? (still called '''Bullialdus A''' and '''Bullialdus B'''). <span class="membersnap">- [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/DannyCaes [[Image:DannyCaes-lg.jpg|16px|DannyCaes]]] [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/DannyCaes DannyCaes] <small>Apr 29, 2017</small></span> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | [ | + | [[Alphabetical%20Index|Named Features]] -- Prev: [[Buisson|Buisson]] -- Next: [[Bunsen|Bunsen]]<br /> |
---- | ---- | ||
This page has been edited 1 times. The last modification was made by <span class="membersnap">- [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/tychocrater [[Image:tychocrater-lg.jpg|16px|tychocrater]]] [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/tychocrater tychocrater]</span> on Jun 13, 2009 3:24 pm - ''afx2u3''</div> | This page has been edited 1 times. The last modification was made by <span class="membersnap">- [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/tychocrater [[Image:tychocrater-lg.jpg|16px|tychocrater]]] [http://www.wikispaces.com/user/view/tychocrater tychocrater]</span> on Jun 13, 2009 3:24 pm - ''afx2u3''</div> | ||
Revision as of 14:42, 15 April 2018
Contents
- 1 Bullialdus - and its two companions (Bullialdus A and B)
- 2 Table of Contents
Bullialdus - and its two companions (Bullialdus A and B)
|
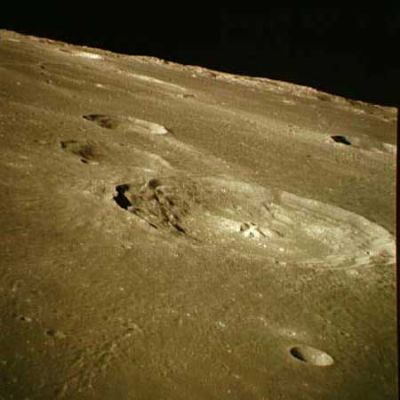
Lat: 20.74°S, Long: 22.36°W, Diam: 60.72 km, Depth: 3.51 km, Rükl: 53, Upper Imbrian | ||
Middle: CLA-F20 from LPOD Photo Gallery,
Right: AS16-119-19091
Table of Contents
Images
LPOD Photo Gallery images Lunar Orbiter Images Apollo Images Wes Higgins
- The so-called "causeway" across the shallow valley Bullialdus W (which is mentioned by Antonin Rukl on his Chart 53), is noticeable near the lower left corner of Lunar Orbiter 4's photograph LOIV-125-h2. It was also captured near the upper margin of Apollo 16's orbital color-Hasselblad frame AS16-119-19104.
- Terrestrial telescopic color-photographs of Bullialdus, made during (or near) Full Moon, show a curious yellowish coloration at Bullialdus's central peak and floor. This curious color is noticeable in many photographs of this crater, such as the one by Michael Hunnekuhl, in the LPOD Spotted Moon.
- Research LOIV and Apollo 16 photographs of the "causeway": Danny Caes
Maps
(LAC zone 94A3) LAC map Geologic map
Description
Elger
(IAU Directions) BULLIALDUS.--A noble object, 38 miles in diameter, forming with its surroundings by far the most notable formation on the surface of the Mare Nubium, and one of the most characteristic ring-plains on the moon. It should be observed about the time when the morning terminator lies on the E. border of the Mare Humorum, as at this phase the best view is obtained of the two deep parallel terrace valleys which run round the bright inner slope of the W. wall, of the crater-row against which they abut on the S.W., and of the massive E. glacis, with its spurs and depressions. The S. border of Bullialdus has been manifestly modified by the presence of the great ring-plain A, a deep irregular formation with linear walls, which is connected with it by a shallow valley. The rampart of Bullialdus rises about 8,000 feet above a concave floor, which sinks some 4,000 feet below the Mare on the W. With the exception of the fine compound central mountain, 3,000 feet high, there are few details in the interior. On the S., is the fine ring-plain B, connected with the S.W. wall near the crater-row by a well-marked valley, and nearly due W. of B is another, a square-shaped enclosure, C, with a very lofty little mountain on the W. side of it, and a crater on its S. wall. In addition to these features, there are many ridges and surface inequalities, very prominent under oblique illumination.
Wikipedia
The yellowish/reddish coloration of the central peak of Bullialdus
This remarkable coloration is captured on the LROC's WAC albedo/color map, see close up of Bullialdus and environs: http://bit.ly/1CPZxT9
Additional Information
- IAU page: Bullialdus
- Depth data from Kurt Fisher database
- Westfall, 2000: 3.51 km
- Viscardy, 1985: 3.51 km
- Cherrington, 1969: 3.44 km
- Measurements of crater topography using Kaguya laser altimeter terrain profile graphs. - LunarJim LunarJim Oct 6, 2011
- Crater Depth:Measurements on 4 axes separated by 45 degrees.
- Zero reference level = Moon average radius.
- Average floor level (average of lowest levels on 4 axes) = -4.72 km
- Average rim height (average of 8 rim data points)= -1.50 km
- Average crater depth (average rim height to average floor level) = 3.22 km
- Deepest point on crater floor (from zero reference level) = -4.75 km
- Max. crater depth (highest point on rim to deepest point on crater floor) = 3.48 km
- Central Peak Height(above average floor level) = 0.8 km
- Central peak height
- Wood, 1971: 1.11 km - tychocrater tychocrater Mar 17, 2008
- Central peak composition: GNTA1, GNTA2, AN & N (Tompkins & Pieters, 1999)
- West rim slope 46° (Pohn, 1963)
- Stratigraphy changed to Upper Imbrian based on Galileo data and crater counts (McEwen et al, 1993)
- Note the wonderfully impacted display (yellow box in the large image version below - click image) of lighter material from this WAC view showing a region northwest of Bullialdus B. Did a chunk from Tycho's (to the south-east) ejecta clip the rim; sending out material across the darker ejecta plain of Bullialdus crater?. There also is an additional feature to look out for here just south of Bullialdus crater itself (red box in larger version image), where upto five fingers of lighter-looking deposits (again, possibly due to ejecta material-chunks from Tycho crater) has directionally, and dynamically, aligned itself back to that crater. LROC images (WAC No.s (left image) M120004880ME and (right image) M117643256ME). Calibrated by LROC_WAC_Previewer- JohnMoore2 JohnMoore2
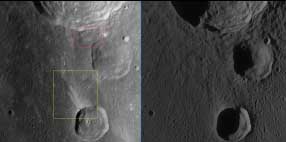
- A certain Whitley discovered several chains of minute craters southeast of Bullialdus, see page 136 in T.W.Webb's Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (Volume 1; The Solar System, chapter THE MOON). - DannyCaes DannyCaes Jul 11, 2015
Nomenclature
- Named for Ismaël Boulliau (September 28, 1605 - November 25, 1694), a French priest, librarian and astronomer. Boulliau's name has apparently also (but incorrectly according to this 19th century French encyclopedia) been spelled Bouillaud. It is for his astronomical and mathematical works that Boulliau is best known. Among them in his Astronomia philolaica, published in 1645 and famous for the passage in which he proposed that the force of gravity follows an inverse-square law.
- According to Whitaker (p. 211), the crater name, in the Latinized form Bullialdus, has continued unchanged since its original use on Riccioli's map.
- Mary Blagg, in her Collated List (1913) noted that the feature name was spelled Bullialdus by Neison, 1876 and Schmidt, but Bulliald by Beer and Mädler (possibly a misprint in her catalog?).
- Curiously, the name is printed and listed as Bouillaud on Sheet 2 of the Army Map Service's LTM series (prepared in 1963), which claims to adhere strictly to the then-current IAU nomenclature. Why the map makers thought the IAU name had been changed to this (incorrect) non-Latinized form is unclear. It does not seem to have been used in that way on any other maps of the period. - JimMosher JimMosher
- I have the 1935 IAU map and catalog where the name appears as Bullialdus; apparently the LTM list is not an error-free transcription. - tychocrater tychocrater Aug 1, 2007
- Why are there no officially recognized names for two pronounced craters south of Bullialdus? (still called Bullialdus A and Bullialdus B). - DannyCaes DannyCaes Apr 29, 2017
Lettered Craters
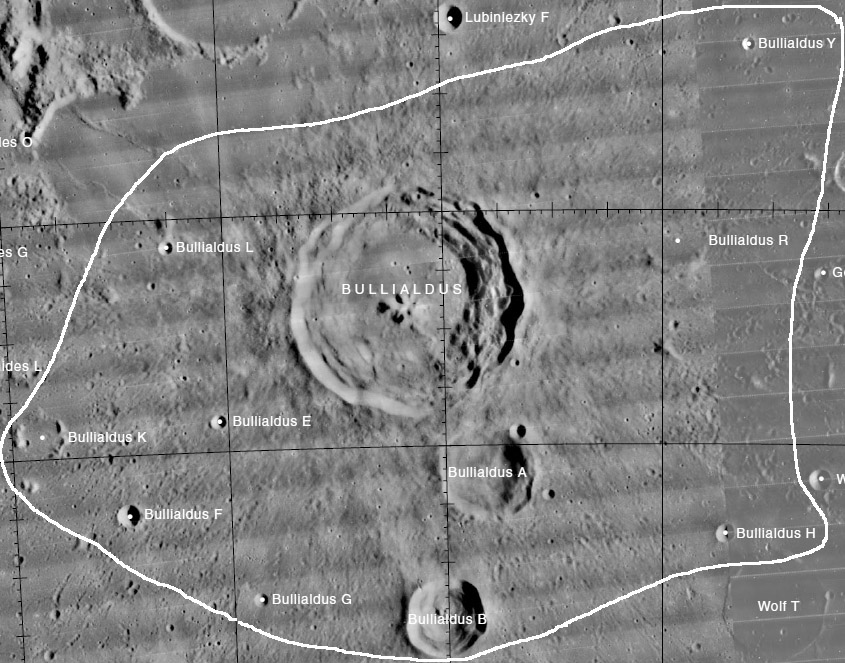
Excerpt from the USGS Digital Atlas of the Moon.
LPOD Articles
Bullialdus' Ridge Clumps and Tadpoles Almost on the Ground Bully for Bullialdus Spotted Moon
Bibliography
- Pieters, C. M. (1991). Strengthening the case for lunar plutons. Geophys. Res. Letters, 18, 2129-2132.
- Klima, R and others (2012) Bullialdus Crater: Correlation between KREEP and local mineralogy 43rd LPSC Conference #2517.
- Moriarty, D. and others (2012) Compositional Heteorgeniety with Lunar Central Peaks 43rd LPSC #2399.
Ismael Boulliau in the Sourcebook Project (William R. Corliss)
- Page 573 in Mysterious Universe, a handbook of astronomical anomalies (1979) :
- The Temporary Stars (David E. Packer, Journal of the British Astronomical Association, 1894).
Named Features -- Prev: Buisson -- Next: Bunsen
This page has been edited 1 times. The last modification was made by - tychocrater tychocrater on Jun 13, 2009 3:24 pm - afx2u3


