Difference between revisions of "Hess"
(Created page with "<div id="content_view" class="wiki" style="display: block"> =Hess= {| class="wiki_table" | Lat: 54.3°S, Long: 174.6°E, Diam: 88 km, Depth: km, Rükl: ''(farside)''<br />...") |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
|} | |} | ||
<div id="toc"> | <div id="toc"> | ||
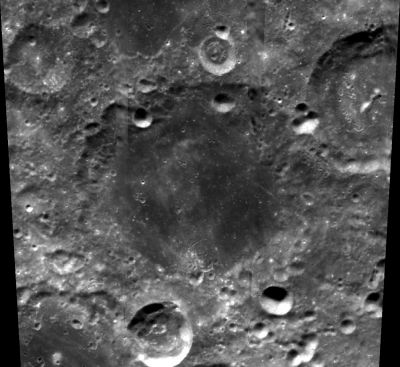
| − | + | [http://www.lpod.org/coppermine/displayimage.php?pid=1989&fullsize=1 [[Image:Normal_hess-clem1.jpg|external image normal_hess-clem1.jpg]]]<br /> ''[http://lpod.org/coppermine/displayimage.php?pos=-1989 Clementine]''<br /> <br /> | |
| − | |||
==Images== | ==Images== | ||
[http://www.lpod.org/coppermine/thumbnails.php?album=search&type=full&search=Hess LPOD Photo Gallery] [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/resources/lunar_orbiter/bin/srch_nam.shtml?Hess%7C0 Lunar Orbiter Images] [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/resources/apollo/search/feature/?feature=Hess Apollo Images]<br /> <br /> | [http://www.lpod.org/coppermine/thumbnails.php?album=search&type=full&search=Hess LPOD Photo Gallery] [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/resources/lunar_orbiter/bin/srch_nam.shtml?Hess%7C0 Lunar Orbiter Images] [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/resources/apollo/search/feature/?feature=Hess Apollo Images]<br /> <br /> | ||
==Maps== | ==Maps== | ||
| − | ''([ | + | ''([[LAC%20zone|LAC zone]] 132A3)'' [http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/images/Lunar/lac_132.pdf USGS Digital Atlas PDF]<br /> <br /> [http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/2490 IAU page]<br /> <br /> |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 18: | Line 17: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
==Nomenclature== | ==Nomenclature== | ||
| − | * This name was added to the IAU nomenclature in [http://the-moon. | + | * This name was added to the IAU nomenclature in [http://the-moon.us/wiki/Menzel%2C%201971#HESS Menzel, 1971]. It honors two men: |
** [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Victor_Franz_Hess Victor Francis Hess] (June 24, 1883 – December 17, 1964) was an Austrian-American physicist. By means of instruments carried aloft in balloons, Hess and others proved that radiation that ionizes the atmosphere is of cosmic origin. For his discovery of cosmic rays he won the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics, shared with Carl David Anderson. | ** [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Victor_Franz_Hess Victor Francis Hess] (June 24, 1883 – December 17, 1964) was an Austrian-American physicist. By means of instruments carried aloft in balloons, Hess and others proved that radiation that ionizes the atmosphere is of cosmic origin. For his discovery of cosmic rays he won the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics, shared with Carl David Anderson. | ||
** [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Harry_Hammond_Hess Harry Hammond Hess] (May 24, 1906 – August 25, 1969) was an American geologist and is considered one of the "founding fathers" of the unifying theory of plate tectonics. He is best known for his theories on sea floor spreading, specifically work on relationships between island arcs, seafloor gravity anomalies, and serpentinized peridotite, suggesting that the convection of the Earth's mantle was the driving force behind this process. This work provided a conceptual base for the development of the theory of plate tectonics. | ** [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Harry_Hammond_Hess Harry Hammond Hess] (May 24, 1906 – August 25, 1969) was an American geologist and is considered one of the "founding fathers" of the unifying theory of plate tectonics. He is best known for his theories on sea floor spreading, specifically work on relationships between island arcs, seafloor gravity anomalies, and serpentinized peridotite, suggesting that the convection of the Earth's mantle was the driving force behind this process. This work provided a conceptual base for the development of the theory of plate tectonics. | ||
** Perhaps it's interesting to include [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wilmot_N._Hess Wilmot N. Hess] (1926-2004; American physicist involved in NASA's Apollo moon missions). | ** Perhaps it's interesting to include [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wilmot_N._Hess Wilmot N. Hess] (1926-2004; American physicist involved in NASA's Apollo moon missions). | ||
| − | * The much smaller astronaut-named crater [ | + | * The much smaller astronaut-named crater [[Hess-Apollo|Hess-Apollo]] (at Apollo-17's landing site) was also named to honor Harry Hess. |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
==LPOD Articles== | ==LPOD Articles== | ||
| Line 29: | Line 28: | ||
<br /> <br /> | <br /> <br /> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | + | </div> | |
Latest revision as of 01:52, 16 April 2018
Contents
Hess
| Lat: 54.3°S, Long: 174.6°E, Diam: 88 km, Depth: km, Rükl: (farside) |
Images
LPOD Photo Gallery Lunar Orbiter Images Apollo Images
Maps
(LAC zone 132A3) USGS Digital Atlas PDF
IAU page
Description
Description: Wikipedia
Additional Information
Nomenclature
- This name was added to the IAU nomenclature in Menzel, 1971. It honors two men:
- Victor Francis Hess (June 24, 1883 – December 17, 1964) was an Austrian-American physicist. By means of instruments carried aloft in balloons, Hess and others proved that radiation that ionizes the atmosphere is of cosmic origin. For his discovery of cosmic rays he won the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics, shared with Carl David Anderson.
- Harry Hammond Hess (May 24, 1906 – August 25, 1969) was an American geologist and is considered one of the "founding fathers" of the unifying theory of plate tectonics. He is best known for his theories on sea floor spreading, specifically work on relationships between island arcs, seafloor gravity anomalies, and serpentinized peridotite, suggesting that the convection of the Earth's mantle was the driving force behind this process. This work provided a conceptual base for the development of the theory of plate tectonics.
- Perhaps it's interesting to include Wilmot N. Hess (1926-2004; American physicist involved in NASA's Apollo moon missions).
- The much smaller astronaut-named crater Hess-Apollo (at Apollo-17's landing site) was also named to honor Harry Hess.
LPOD Articles
Bibliography