D'Arsonval
Contents
[hide]D'Arsonval
| Lat: 10.31°S, Long: 124.59°E, Diam: 30.36 km, Depth: km, Rükl: (farside) | |
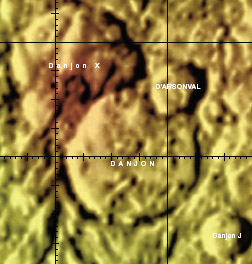
Right: Color-coded topography LAC 83 image from USGS Digital Atlas. D'Arsonval crater is the smaller-looking crater that has impacted upon the north-eastern sector of the much larger crater, Danjon, seen in the centre of the left photo.
Images
LPOD Photo Gallery Lunar Orbiter Images Apollo Images (to get orbital Apollo photographs of D'Arsonval, please visit the LPI's list of adjacent crater Danjon).
- D'Arsonval and its larger companion Danjon were captured in this shadowless orbital photograph made during the mission of Apollo 8: AS8-17-2739.
- HiRes-scan of Apollo 8 photograph: David Woods and Frank O'Brien (Apollo 8 Flight Journal).
- D'Arsonval and Danjon were also captured by Apollo 13; near the upper left corner of AS13-60-8632.
- D'Arsonval with shadows: Apollo 17's orbital panoramic ITEK-camera frame AS17-P-2787 (near the frame's right margin).
- Research Apollo 13 and Apollo 17 photography: Danny Caes
Maps
Description
Wikipedia
Additional Information
- IAU page: D'Arsonval
Nomenclature
Named for Jacques-Arsène d'Arsonval (June 8, 1851 - December 13, 1940), a French biophysicist and inventor of the moving-coil galvanometer and probably of the thermocouple ammeter. Along with Nikola Tesla, d'Arsonval was an important contributor to the emerging field of electrophysiology, the study of the effects of electricity on biological organisms, in the nineteenth century. In 1881, d'Arsonval proposed tapping the thermal energy of the ocean.
LPOD Articles
Bibliography
Named Features -- Prev: D'Arrest -- Next: Darwin