Difference between revisions of "RoI - Anaxagoras Crater"
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div id="content_view" class="wiki" style="display: block"> | <div id="content_view" class="wiki" style="display: block"> | ||
=Anaxagoras Crater= | =Anaxagoras Crater= | ||
| − | ''(Tier 1 [ | + | ''(Tier 1 [[Cx35|Region of Interest]] for Constellation Program)''<br /> <br /> |
==Official NASA Overview== | ==Official NASA Overview== | ||
[[Image:ROI_-_Anaxagoras_Crater.JPG|ROI_-_Anaxagoras_Crater.JPG]]<br /> ''source: NASA [http://ser.sese.asu.edu/LSM/files/Cx-LROC-Tier1-FINAL.pdf Cx-LROC Tier 1 Targets] (PDF); see expanded details below''<br /> <div id="toc"> | [[Image:ROI_-_Anaxagoras_Crater.JPG|ROI_-_Anaxagoras_Crater.JPG]]<br /> ''source: NASA [http://ser.sese.asu.edu/LSM/files/Cx-LROC-Tier1-FINAL.pdf Cx-LROC Tier 1 Targets] (PDF); see expanded details below''<br /> <div id="toc"> | ||
| − | + | <br /> | |
| − | |||
==Scientific Rationale== | ==Scientific Rationale== | ||
===Crater central peak=== | ===Crater central peak=== | ||
| − | The central peak material of [ | + | The central peak material of [[Anaxagoras|Anaxagoras]] is believed to consist of pure anorthosite, which, by definition, is a coarse-grained, mafic ('''MA'''gnesium + Iron '''F'''err'''IC''') igneous plutonic rock -- one that has formed at considerable depth within a planet or moon -- approaching 98% volume in plagioclase (a feldspar mineral). The anorthosite presence is believed to be a signature of differentiaton processes (its low density caused it to float to the top forming a thin crust) in a magma ocean that once encompassed the early-forming Moon. Recent reflectance spectral data obtained by the Japanese Kaguya/Selene spacecraft which launched three years ago (and subsequently crashed onto the lunar surface in June 2009), points to the possibility of a global layer of pure anorthositic rocks in the upper crust of the Moon. Signatures of the anorthosite deposits, composed of nearly 100% volume plagioclase, particularly showed up in areas of crater central peaks, walls, ejecta and basin rings, and is suggested as being ubiquitously present within the depth range from 3 km to at least 30 km in a global perspective. Whether this latter finding is the case or that the pure anorthorsitic signatures are due to discrete intusive bodies is still uncertain, however, further analyses around such regions are certain to provide a constraint on models of lunar magma ocean formation and formation of the Moon. <span class="membersnap">- JohnMoore2</span><br /> <br /> |
===Impact process=== | ===Impact process=== | ||
| − | Some of the central peak material of Anaxagoras overlies the south-western sector of its terraced crater walls. The impact processes involved caused material (anothorsite in this case) at depth in rebounding upwards to form the central peak; suggesting that its resultant asymmetric appearance may be due to collapse sideways of the material. Other influential mechanisms, like impactor direction or underlying rock material, may have played a role in the central peak's appearance, so Anaxagoras provides a unique region in which to better understand peak formation as a whole. <span class="membersnap">- | + | Some of the central peak material of Anaxagoras overlies the south-western sector of its terraced crater walls. The impact processes involved caused material (anothorsite in this case) at depth in rebounding upwards to form the central peak; suggesting that its resultant asymmetric appearance may be due to collapse sideways of the material. Other influential mechanisms, like impactor direction or underlying rock material, may have played a role in the central peak's appearance, so Anaxagoras provides a unique region in which to better understand peak formation as a whole. <span class="membersnap">- JohnMoore2</span><br /> <br /> <br /> |
{| class="wiki_table" | {| class="wiki_table" | ||
| | | | ||
| − | [http://the-moon.us/wiki/file/detail/anaxagoras-large.jpg [[Image: | + | [http://the-moon.us/wiki/file/detail/anaxagoras-large.jpg [[Image:Anaxagoras-small.jpg|anaxagoras-small.jpg]]]<br /> |
| | | | ||
'''Left:''' [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/resources/lunarorbiter/images/preview/4140_h2.jpg Lunar Orbiter 4 LO-4140-H2] image from [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/ LPI].<br /> '''Middle:''' Geological sketch map of Anaxagoras -- adapted from J. B. Murray's 1979 paper [http://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu//full/1980M%26P....22..269M/0000269.000.html "Oscillating Peak Model of Basin and Crater Formation", page 296] (NB. Sketch has been orientated to suit side-images that have North up and West left).<br /> '''Right:''' [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/resources/mapcatalog/usgs/I1062/ Geologic Map] image (1978) from [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/ LPI]. ''Click image for larger view''<br /> | '''Left:''' [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/resources/lunarorbiter/images/preview/4140_h2.jpg Lunar Orbiter 4 LO-4140-H2] image from [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/ LPI].<br /> '''Middle:''' Geological sketch map of Anaxagoras -- adapted from J. B. Murray's 1979 paper [http://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu//full/1980M%26P....22..269M/0000269.000.html "Oscillating Peak Model of Basin and Crater Formation", page 296] (NB. Sketch has been orientated to suit side-images that have North up and West left).<br /> '''Right:''' [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/resources/mapcatalog/usgs/I1062/ Geologic Map] image (1978) from [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/ LPI]. ''Click image for larger view''<br /> | ||
| Line 20: | Line 19: | ||
{| class="wiki_table" | {| class="wiki_table" | ||
| | | | ||
| − | [http://the-moon.us/wiki/file/detail/anaxagoras2-large.jpg [[Image: | + | [http://the-moon.us/wiki/file/detail/anaxagoras2-large.jpg [[Image:Anaxagoras-small2.jpg|anaxagoras-small2.jpg]]]''Click image for larger view''<br /> |
|} | |} | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 46: | Line 45: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | <br /> | + | <br /> </div> |
Latest revision as of 20:32, 16 April 2018
Contents
Anaxagoras Crater
(Tier 1 Region of Interest for Constellation Program)
Official NASA Overview
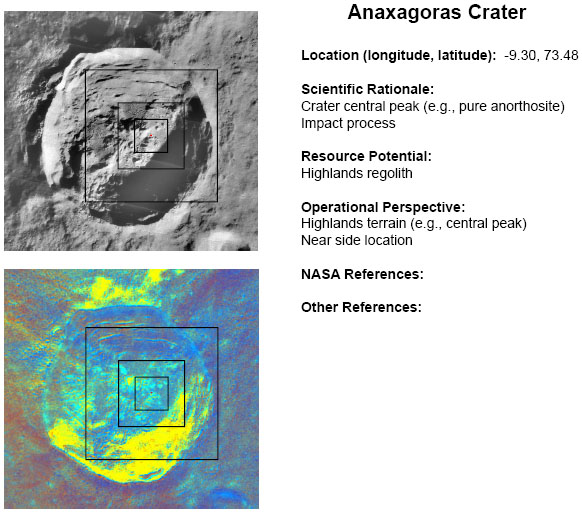
source: NASA Cx-LROC Tier 1 Targets (PDF); see expanded details below
Scientific Rationale
Crater central peak
The central peak material of Anaxagoras is believed to consist of pure anorthosite, which, by definition, is a coarse-grained, mafic (MAgnesium + Iron FerrIC) igneous plutonic rock -- one that has formed at considerable depth within a planet or moon -- approaching 98% volume in plagioclase (a feldspar mineral). The anorthosite presence is believed to be a signature of differentiaton processes (its low density caused it to float to the top forming a thin crust) in a magma ocean that once encompassed the early-forming Moon. Recent reflectance spectral data obtained by the Japanese Kaguya/Selene spacecraft which launched three years ago (and subsequently crashed onto the lunar surface in June 2009), points to the possibility of a global layer of pure anorthositic rocks in the upper crust of the Moon. Signatures of the anorthosite deposits, composed of nearly 100% volume plagioclase, particularly showed up in areas of crater central peaks, walls, ejecta and basin rings, and is suggested as being ubiquitously present within the depth range from 3 km to at least 30 km in a global perspective. Whether this latter finding is the case or that the pure anorthorsitic signatures are due to discrete intusive bodies is still uncertain, however, further analyses around such regions are certain to provide a constraint on models of lunar magma ocean formation and formation of the Moon. - JohnMoore2
Impact process
Some of the central peak material of Anaxagoras overlies the south-western sector of its terraced crater walls. The impact processes involved caused material (anothorsite in this case) at depth in rebounding upwards to form the central peak; suggesting that its resultant asymmetric appearance may be due to collapse sideways of the material. Other influential mechanisms, like impactor direction or underlying rock material, may have played a role in the central peak's appearance, so Anaxagoras provides a unique region in which to better understand peak formation as a whole. - JohnMoore2
|
Left: Lunar Orbiter 4 LO-4140-H2 image from LPI. |
Additional Information
LROC Links
- Featured Image -- Exposed Fractured Bedrock in the Central Peak of the Anaxagoras Crater
LPOD Articles
Blue Dots, White Rocks, Stratigraphy of Brightness, North Polar Rays, Was Anaxagoras an Oblique Impact, Page One of a New Book, Color Me Anorthosite.
General Bibliography
- Anderson, T. et al (2010). Target and Projectile:Material Effects on Crater Excavation and Growth from 41st Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (2010)
- Charlier, B. et al (2010). Anorthosite in the Sept Iles Layered Intrusion (Canada): Ideas for the Formation of the Lunar Crust from 41st Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (2010)
- Edmunson, J. et al (2010). Yttrium Silicate in Lunar Troctolitic Anorthosite 76335 from 41st Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (2010)
- Hermalyn, B. (2010). Early-Stage Coupling for Oblique Impacts in granualr Material from 41st Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (2010)
- Korotev, R. L. et al (2010). On the Origin of the Moon's Feldspathic Highlands, Pure Anorthosite, and the Feldspathic Lunar Meteorites from 41st Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (2010)
- Miura, Y. et al (2010). Calcium-Rich Plagioclases Formed by Giant Impact Event to the Lunar Crust from 41st Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (2010)
- Parmentier, E.M and Yan Liang, (2010). Formation of Pure Anorthorsite During Magma Ocean Solidification: Implications for the Melt-Solid Segregation Process from 41st Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (2010)
- Uemoto, K. et al (2010). Purest Anorthosite Distribution in the Lunar South Pole-Aitken Basin Derived from Selene Multiband Imager from 41st Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (2010)
- Ohtake, M. et al (2009). Anorthosite with 100% Plagioclase on the Moon Detected by the Selenemultiband Imager from 40th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (2009)
- Ohtake, M. et al. (2009). The Global Distribution of Pure Anorthosite on the Moon ( Nature 461, 236-240, 10 September 2009)
- Murray, J. B. (1979). Oscillating Peak Model of Basin and Crater Formation
- Wood, J. A. et al (1970). Lunar Anorthosites - Science 30 January 1970: Vol. 167. no. 3918, pp. 602 - 604 DOI: 10.1126/science.167.3918.602. (1970).

