Difference between revisions of "Avicenna"
(Created page with "<div id="content_view" class="wiki" style="display: block"> =Avicenna= {| class="wiki_table" | Lat: 39.7°N, Long: 97.2°W, Diam: 74 km, Depth: 3.26 km, Rükl: ''(farside)'...") |
|||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
* Named for [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Avicenna Abu Ali Al-Hussein Ibn Abdallah] (980-1037), also known as Ibn Seena and Avicenna, a Persian philosopher and, according to the IAU citation the "greatest physician of medieval times", who among his other accomplishments suggested the speed of light must be finite. | * Named for [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Avicenna Abu Ali Al-Hussein Ibn Abdallah] (980-1037), also known as Ibn Seena and Avicenna, a Persian philosopher and, according to the IAU citation the "greatest physician of medieval times", who among his other accomplishments suggested the speed of light must be finite. | ||
| − | * '''Avicenna''' was among the long list of farside feature names approved by the [/IAU IAU] in 1970 and published in [http://the-moon. | + | * '''Avicenna''' was among the long list of farside feature names approved by the [/IAU IAU] in 1970 and published in [http://the-moon.us/wiki/Menzel%2C%201971#Avicenna Menzel, 1971]. |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
==LPOD Articles== | ==LPOD Articles== | ||
Revision as of 20:09, 11 April 2018
Contents
Avicenna
| Lat: 39.7°N, Long: 97.2°W, Diam: 74 km, Depth: 3.26 km, Rükl: (farside) |
Table of Contents
[#Avicenna Avicenna]
[#Avicenna-Images Images]
[#Avicenna-Maps Maps]
[#Avicenna-Description Description]
[#Avicenna-Description: Wikipedia Description: Wikipedia]
[#Avicenna-Additional Information Additional Information]
[#Avicenna-Nomenclature Nomenclature]
[#Avicenna-LPOD Articles LPOD Articles]
[#Avicenna-Bibliography Bibliography]
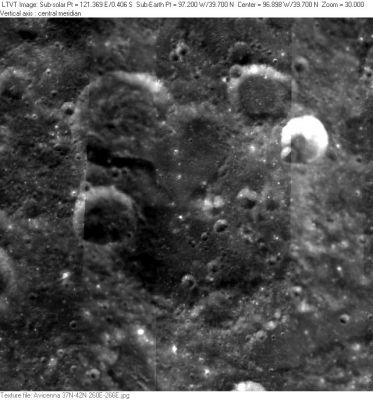
Clementine Avicenna is the large crater in the center. The smaller craters visible here are not named with the exception of 21-km diameter Avicenna R, a very small piece of which can be seen below center along the left margin.
Images
LPOD Photo Gallery Lunar Orbiter Images
- Avicenna was photographed by Lunar Orbiter IV, see frame LO-IV-188-med. On this photograph, Avicenna's location is north (or "above") the Lorentz-Nernst-Rontgen group (captured at the upper half of the frame, near the sunrise terminator).
- See also LO-IV-190-med, in which Avicenna and the Lorentz-Nernst-Rontgen group were captured at the lower left part of the frame. In this photograph, a remarkable "groove" is noticeable north of Avicenna, which runs north-northwest toward an unnamed crater between Rynin and Chapman.
- Research Lunar Orbiter IV photography: Danny Caes
Maps
([/LAC%20zone LAC zone] 36C1)
Description
Description: Wikipedia
Additional Information
- Depth data from [/Kurt%20Fisher%20crater%20depths Kurt Fisher database] :
- Cherrington, 1969: 3.26 km
- Remarkable "groove" north of Avicenna, which runs north-northwest toward an unnamed crater between Rynin and Chapman. This "groove" is vaguely depicted on page 73 (LAC 36) in the Clementine Atlas of the Moon (revised edition, 2012). - DannyCaes DannyCaes Feb 12, 2014
Nomenclature
- Named for Abu Ali Al-Hussein Ibn Abdallah (980-1037), also known as Ibn Seena and Avicenna, a Persian philosopher and, according to the IAU citation the "greatest physician of medieval times", who among his other accomplishments suggested the speed of light must be finite.
- Avicenna was among the long list of farside feature names approved by the [/IAU IAU] in 1970 and published in Menzel, 1971.
LPOD Articles
Bibliography
This page has been edited 1 times. The last modification was made by - tychocrater tychocrater on Jun 13, 2009 3:24 pm - afx3u2