Nernst
Contents
[hide]Nernst - together with Rontgen on the floor of Lorentz
|
Lat: 35.3°N, Long: 94.8°W, Diam: 116 km, Depth: km, Rükl: (farside); Nectarian/Imbrian |
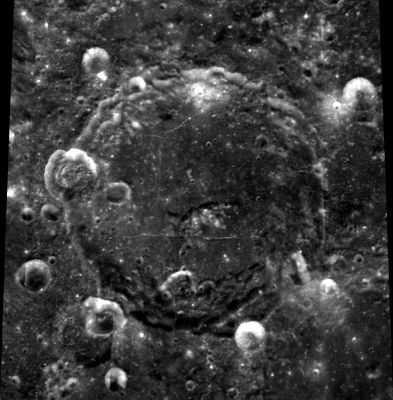
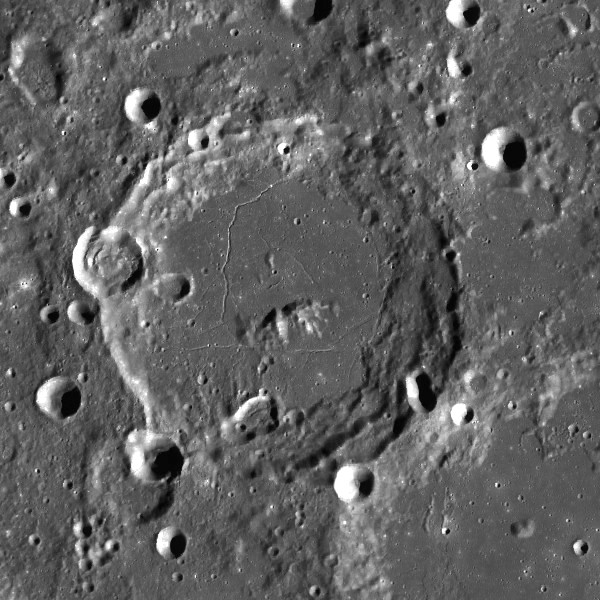
left: Clementine . right: LROC
In both photographs, Nernst is the central crater, the crater at the lower right corners of both frames is Rontgen.
Images
LPOD Photo Gallery Lunar Orbiter Images
See page Lorentz for four Lunar Orbiter 4 photographs of Nernst (this crater is part of the Lorentz-Nernst-Rontgen group).- DannyCaes Feb 10, 2014
Maps
(LAC zone 36C4) USGS Digital Atlas PDF
Description
Description: Wikipedia
Additional Information
- A small dark halo/pyroclastic deposits occurs on a fracture. Rosanova et al, 1998
Nomenclature
Walther Hermann Nernst (June 25, 1864 – November 18, 1941) was a German chemist who is known for his theories behind the calculation of chemical affinity as embodied in the third law of thermodynamics, for which he won the 1920 Nobel Prize in chemistry. Nernst helped establish the modern field of physical chemistry and contributed to electrochemistry, thermodynamics, solid state chemistry and photochemistry. He is also known for developing the Nernst equation.
Rimae Nernst (an unofficial name from D.Caes for the system of rilles on the floor of Nernst).
LPOD Articles
Bibliography