Difference between revisions of "Compton"
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
==Additional Information== | ==Additional Information== | ||
| − | * From the shadows in [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/resources/lunarorbiter/frame/?5181 LO-V-181M], the central peaks of '''Compton''' rise about 2700 m above the floor. The crater appears to be somewhat deeper, but the shadows are not suitable for a measurement of its depth. <span class="membersnap">- | + | * From the shadows in [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/resources/lunarorbiter/frame/?5181 LO-V-181M], the central peaks of '''Compton''' rise about 2700 m above the floor. The crater appears to be somewhat deeper, but the shadows are not suitable for a measurement of its depth. <span class="membersnap">- JimMosher</span> |
| − | * Frame '''2700r''' from the [http://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/Missions/Galileo_mission.html Galileo] fly-by of the Moon shows the western part of '''Compton''' with a low [http://the-moon.us/wiki/sun%20angle sun angle] from the west. The shadows falling on the floor indicate a considerable variation in the height of the western rim, ranging from about 1300 m in north to 4100 m in south, with a typical value of about 3200 m near the middle. <span class="membersnap">- | + | * Frame '''2700r''' from the [http://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/Missions/Galileo_mission.html Galileo] fly-by of the Moon shows the western part of '''Compton''' with a low [http://the-moon.us/wiki/sun%20angle sun angle] from the west. The shadows falling on the floor indicate a considerable variation in the height of the western rim, ranging from about 1300 m in north to 4100 m in south, with a typical value of about 3200 m near the middle. <span class="membersnap">- JimMosher</span> |
* Three small pyroclastic deposits (area = 24, 45 & 5 km^2). Gaddis, L. (1999) [http://astrogeology.usgs.gov/Projects/LunarPyroclasticVolcanism/lunpyroWebDb.html Lunar Pyroclastic Volcanism Project]. | * Three small pyroclastic deposits (area = 24, 45 & 5 km^2). Gaddis, L. (1999) [http://astrogeology.usgs.gov/Projects/LunarPyroclasticVolcanism/lunpyroWebDb.html Lunar Pyroclastic Volcanism Project]. | ||
* Four dark halo/pyroclastic deposits located on floor fractures; three are 2-6 km in diameter, the others is ~15 km wide. [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/LPSC98/pdf/1710.pdf Rosanova et al, 1998] | * Four dark halo/pyroclastic deposits located on floor fractures; three are 2-6 km in diameter, the others is ~15 km wide. [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/LPSC98/pdf/1710.pdf Rosanova et al, 1998] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:08, 16 April 2018
Contents
Compton Basin
(unofficial name; IAU crater name: Compton; 162 km diam)
|
Lat: 55.3°N, Long: 103.8°E, Main ring diam: 175 km, Depth: 3.2 km, Rükl: (farside), Lower Imbrian |

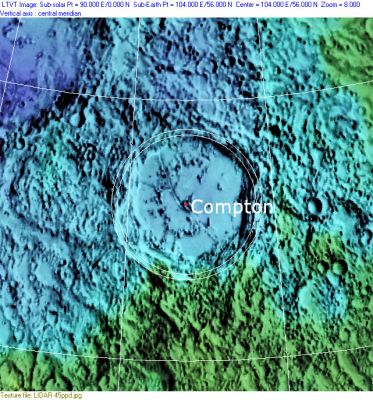
Left: LO-V-181M
Right: Clementine, Clementine LIDAR Altimeter texture from PDS Map-a-Planet remapped to north-up aerial view by LTVT. The dot is the center position and the white circle the main ring position from Chuck Wood's Impact Basin Database. Grid spacing = 10 degrees.
Images
LPOD Photo Gallery Lunar Orbiter Images
- Compton was photographed during the mission of Apollo 16, on color-Hasselblad film, such as frame AS16-121-19445. In this frame, Compton's location is a little bit to the right of centre.
- AS16-M-3019 is one of Apollo 16's Fairchild-camera photographs which show Compton near the limb at lower right. This photograph was made during Trans Earth Coast (TEC).
- Research Apollo 16 photography: Danny Caes
Maps
(LAC zone 16D1) USGS Digital Atlas PDF
Basin Classification
(description of terms and most numeric basin data from Wood, C.A. (2004) Impact Basin Database)
| Certainty of Existence |
USGS Age |
Wilhelms Age Group |
Ring Diameters |
Mare Thickness |
Mascon |
| Certain |
Lower Imbrian |
80, 175 km |
No |
Description
Peak ring basin
Wikipedia
Additional Information
- From the shadows in LO-V-181M, the central peaks of Compton rise about 2700 m above the floor. The crater appears to be somewhat deeper, but the shadows are not suitable for a measurement of its depth. - JimMosher
- Frame 2700r from the Galileo fly-by of the Moon shows the western part of Compton with a low sun angle from the west. The shadows falling on the floor indicate a considerable variation in the height of the western rim, ranging from about 1300 m in north to 4100 m in south, with a typical value of about 3200 m near the middle. - JimMosher
- Three small pyroclastic deposits (area = 24, 45 & 5 km^2). Gaddis, L. (1999) Lunar Pyroclastic Volcanism Project.
- Four dark halo/pyroclastic deposits located on floor fractures; three are 2-6 km in diameter, the others is ~15 km wide. Rosanova et al, 1998
- Inner mare patches Imbrian age and 4-4.5 wt% FeO content. Younger maria around outer edges (Gillis and Spudis, 1996).
- First described as a basin by Hartmann & Wood (1971).
- At favorable librations, Compton can be seen straddling the limb, but it does not seem to have been recognized in Earth-based observations.
- Telescopic observers of the moon might look for the central peaks of Compton, which are visible during favourable libration! See LPOD Peaking over the Limb and discussions.
Weird stratification at Compton's floor
- The eastern region of the floor of Compton shows some sort of weird stratification: http://bit.ly/2DeCf2X
Nomenclature
- The IAU crater name honors two men:
- Arthur Holly Compton (September 10, 1892 – March 15, 1962) was an American physicist who won the Nobel Prize in Physics (1927) for discovery of the Compton effect. In 1922, Compton found that X-rays wavelength increases due to scattering of the radiant energy by "free electrons". Scattered quanta have less energy than the quanta of the original ray. This discovery, known as the "Compton effect," demonstrates the "particle" concept of electromagnetic radiation.
- Karl Taylor Compton (September 14, 1887 – June 22, 1954) was a prominent American physicist and president of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) from 1930 to 1948.
- The impact basin was named after the crater.
- Compton was among the long list of farside names added to the IAU nomenclature in Menzel, 1971.
- Rimae Compton (an unofficial name from D.Caes for the system of rilles on the floor of Compton).
LPOD Articles
- Peak Rings
- Peaking over the Limb (terrestrial photograph of Compton's central peak).
Bibliography
- Joliff, B. L. et al (2011). Compton-Belkovich: Nonmare, Silicic Volcanism on the Moon’s Far Side – 42nd LPSC Conference (Mar), 2011.
- Tran, T. et al (2011). Morphology of Lunar Volcanic Domes from LROC – 42nd LPSC Conference (Mar), 2011.